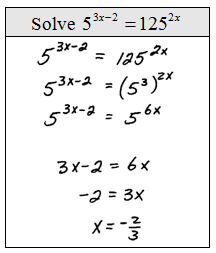Smart Ways to Solve Exponential Equations
Understanding Exponential Equations
Exponential equations are crucial in various fields like mathematics, finance, and biology. These equations typically involve variables in the exponent and can model real-world phenomena such as population growth and radioactive decay. To effectively tackle **solving exponential equations**, a primary understanding of the **properties of exponents** is essential. Exponential equations can often be expressed in the form of a^x = b, where both a and b are positive numbers. The general strategy revolves around **converting between exponential and logarithmic forms**, enabling us to isolate the variable.
Properties of Exponents
To solve exponential equations, one must first master the **properties of exponents**. These fundamental rules guide how to manipulate exponent expressions, enabling simplification before attempting to isolate the variable. For instance, products and quotients can be expressed as sums and differences of exponents: a^m * a^n = a^(m+n) and a^m / a^n = a^(m-n). Knowing these properties not only facilitates **solving for x in exponential equations** but also helps visualize their behavior on graphs.
Logarithmic Functions and Their Application
Logarithmic functions serve as the inverses of exponential functions and are indispensable in **solving exponential equations**. To convert an exponential equation into a logarithmic form, you can employ the rule: if a^b = c, then <code log_a(c) = b. This conversion can often resolve challenges associated with isolating the variable, especially when the bases are different. When dealing with complex situations like **exponential equations with different bases**, applying the **properties of logarithms** is a common technique to unify the bases, making the equation solvable.
Techniques for Solving Exponential Equations
To effectively solve exponential equations, various techniques come into play. One of the most common approaches is rewriting equations into a compatible format. Additionally, computation strategies like numerical methods and algebraic manipulations prove beneficial for equations that resist neat solutions.
Using Logarithms to Isolate Variables
One of the excellent strategies in **solving exponential equations using logarithms** is utilizing logarithmic identities. Consider the example \(2^x = 32\). By rewriting the equation as \(x = log_2(32)\), you simplify your calculations significantly. This approach is especially advantageous for equations featuring bases greater than one, where exact calculations may be cumbersome at first glance.
Understanding Exponential Growth and Decay
Learning about the **characteristics of exponential growth and decay** is particularly vital when dealing with applications. For instance, in finance, you might consider how investments grow with compounded interest—a classic case of exponential growth. Conversely, in fields like biology, understanding how populations decline due to limited resources typically relates to exponential decay models. Recognizing these behaviors can provide critical insights when analyzing more complex **exponential equation word problems**.
Graphing and Visualizing Exponential Equations
The correlation between graphical representations and understanding exponential equations cannot be overstated. Graphing **exponential functions** allows mathematicians to find solutions visually, revealing intersections and asymptotic behavior where applicable. This visualization can be especially useful for students who need to bridge theory with practical analysis.
Graph Transformations of Exponential Functions
Transformations—like shifting, stretching, or reflecting—play significant roles in graphing exponential functions. For example, the function \(f(x) = a(2^x) + k\) indicates a vertical shift determined by \(k\). These transformations directly affect the function’s output, providing clarity about growth rates and convergence towards asymptotes that play crucial roles in understanding **complex exponential equations**.
Exploring Exponential Regression
Exponential regression methods help in predicting trends, particularly in datasets that exhibit **exponential growth** or decay. By leveraging statistical models, one can effectively create a prediction model based on available data points, proving crucial for real-world applications in fields ranging from economics to environmental science. These methods often utilize logarithmic transformations to linearize the data before regression analysis.
Applications of Exponential Equations in Real Life
Exponential equations transcend abstract mathematics, finding significant applications in everyday contexts—be it finance through calculating compound interests or biology when modeling population growth dynamics. The relationship between variables often utilized in **exponential models in real life** manifests in a plethora of scenarios.
Exponential Equations in Finance
In finance, understanding exponential equations is instrumental, especially in compound interest scenarios. The fundamental formula for compound interest can be expressed as \(A = P(1 + r/n)^{nt}\), demonstrating the exponential growth of investments over time. This knowledge allows both individuals and businesses to harness their resources more effectively, maximizing returns based on their financial strategies.
Exponential Growth in Biology
In biology, exponential equations are frequently applied to model populations and the spread of diseases. For instance, the formula \(N(t) = N_0 e^{rt}\) encapsulates population dynamics, where \(N(t)\) is the future population, \(N_0\) is the initial population, and \(r\) is the growth rate. This foundational understanding leads to predicting outcomes efficiently in fields like conservation biology and epidemiology.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the **properties of exponents** is essential when working with exponential equations.
- **Logarithmic functions** serve as vital tools to solve and manipulate these equations.
- Simplifying and rewriting equations before attempting to solve can unlock challenges presented by more complex forms.
- Graphing provides valuable insights and aids in visualizing behaviors and potential solutions.
- Recognizing real-life applications bridges the gap between theoretical concepts of exponentials and tangible results.
FAQ
1. What are the main types of exponential equations?
Exponential equations can be categorized generally into two types: growth and decay. Exponential growth equations, such as \(A = A_0 e^{rt}\), often represent populations, while decay equations model processes like radioactive decay. Recognizing the type is essential for finding the correct approach to solve them effectively.
2. How do logarithms assist in solving exponential equations?
Logarithms convert exponential equations into linear forms, enabling easy isolation of the variable. By using properties of logarithms, particularly for conversions between exponential and logarithmic forms, one can tackle equations like \( 2^x = 16 \) efficiently by rewriting it as \( x = log_2(16) \).
3. Can exponential equations be solved using numerical methods?
Yes, numerical methods such as Newton’s method or bisection method can be effective for solving more complex exponential equations where analytical solutions are challenging. These algorithms iteratively approximate solutions, leading to accurate results for real-world applications.
4. How do transformations affect exponential functions?
Transformations alter the appearance and characteristics of exponential functions on graphs. Vertical and horizontal shifts, stretches, and reflections modify the function, impacting outputs significantly and helping to visualize equations better for analysis.
5. What real-world applications rely on understanding exponential equations?
Exponential equations are crucial in various fields, notably in finance for compound interest calculations, and in biology for modeling populations and disease outbreaks. Understanding these applications allows for better decision-making based on mathematical predictions and analyses.
Reinforcing these concepts equips learners with the ability to approach and solve exponential equations confidently while linking them back to real-world scenarios and practical applications.